Describe How Electronegativity Differences Are Used to Predict
Ability to predict. Predict the partial positive and partial negative ends of a given bond formed between any two of the elements listed in Objective 2 above without the use of a table of electronegativities or a periodic table.

Polar Bonds Molecules Objectives Describe How Electronegativity Values Determine The Distribution Of Charge In A Polar Molecule Describe How Electronegativity Ppt Download
Differences in element electronegativities may be used to predict the type of bonding ionic or covalent in a substance.

. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons within its bonds the larger its electronegativity value. Standard 113 Use the periodic table and electronegativity differences of elements to predict the types of bonds that are formed between atoms during chemical reactions and write the names of chemical compounds including polyatomic ions using the IUPAC criteria. Cite at least one example of.
Similarly you may ask what role does electronegativity play in. A small electronegativity difference leads to a polar covalent bond. Note that this usually only applies to covalent and ionic bonds.
Construct an argument to explain how electronegativity affects the polarity of basic chemical molecules. The Pauling Scale is used to assign electronegativity to. If the difference in electronegativity is between 04 and 17 the character of the bond is polar covalent.
The electrons in a polar bond tend to spend more time. Polar Covalent is the name used to describe bonds that have both ionic and covalent character because the electrons are shared unequally. PS114 Use Lewis dot structures and electronegativity differences to predict the polarities of simple molecules linear bent trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal tetrahedral.
Whether a bond is ionic nonpolar covalent or polar covalent can be estimated by by calculating the absolute value of the difference in electronegativity ΔEN of two bonded atoms. The absolute values of the electronegativity differences between the atoms in the bonds HH HCl and NaCl are 0 nonpolar 09 polar covalent and 21 ionic respectively. An atom with high electronegativity attracts electrons strongly while an atom with low electronegativity attracts them weakly.
A large electronegativity difference leads to an ionic bond. ΔEN 05the bond is non-polar covalent. Define and understand the concept of electronegativity describe trends in electronegativity across the periodic table use Linus Paulings numerical values to compare the electronegativity of different elements list factors that affect electronegativity predict the type of bonding that is likely to occur from differences in electronegativity.
Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons or electron density within a bond. When the difference is very small or zero the bond is covalent and nonpolar. Electronegativity values are used to predict how different atoms will behave when bonded to each other making this an important skill in basic chemistry.
Scales of electronegativity values are used by chemists to describe numerous chemical features such as chemical mechanisms bond polarity band gap atomic hardness etc. 05 ΔEN 2the bond is polar covalent. Generally the farther apart two elements are on the periodic table the more ionic the bond character and the closer together they are the less ionic the bond is.
In a simple molecule like HCl if the bond is polar so also is the whole molecule. Describe how differences in electronegativity give rise to bond polarity. Electronegativity differences can be used to predict how shared electrons are distributed between the two nuclei in a bond.
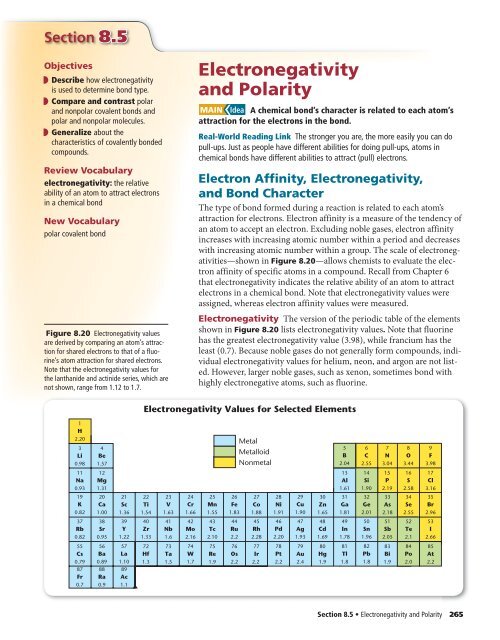
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract the electrons when the atom is part of a compound. Periodic Trends - Electronegativity Atomic Radius Ionization Energy History of the Periodic TableThis bundle of Power Point Presentations includes 47 slides of information that teach the following objectivesDescribe how the Periodic Table is arranged todayExplain basic similarities and differences among groups and periods on the Periodic TableLocate and label common. The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity.
Polar bonds and polar molecules. 1 Q1 3 IMF and Graphical Representations. Electronegativity differs from electron affinity because electron affinity is the actual energy released when an atom gains an electron.
Electronegativity is not measured in energy units but is rather a relative scale. Electronegativity difference between two atoms in a bond can determine what type of bond is used. When it is large the bond is polar covalent or ionic.
If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 17 the character of the bond will be ionic. The degree to which electrons are shared between atoms varies from completely equal pure covalent bonding to not at all ionic bonding. Explain the difference between the models for polar bonds and nonpolar bonds.
Define the term electronegativity. The general rule is that. No electronegativity difference between two atoms leads to a pure non-polar covalent bond.
The difference in electronegativity Δ EN between bonded atoms can indicate whether the bond is nonpolar polar covalent or ionic. ΔEN 2the bond is ionic. The larger the differences in electronegativity between two bonded atoms the more polar the bond.
Use the periodic table to display general trends in electronegativity within periods and groups.
Electronegativity And Polar Bonds
Comments
Post a Comment